Benign skin lesions in general surgery
Autore:Benign skin lesions are non-cancerous growths or abnormalities on the skin that can present in various forms, such as moles, cysts, lipomas, and skin tags. While they are generally harmless, some may require medical attention or removal for specific reasons. General surgeons often play a vital role in assessing and managing these lesions, ensuring both safety and optimal outcomes for patients.
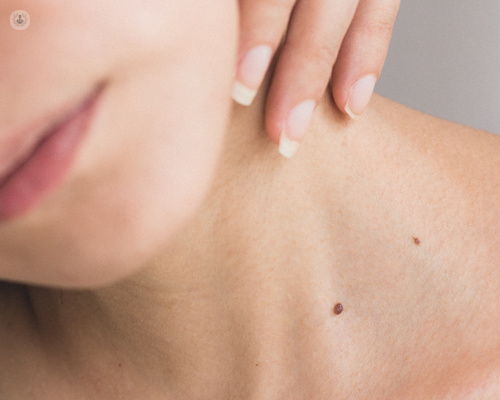
What are the common types of benign skin lesions?
Benign skin lesions can appear in different shapes, sizes, and textures. Some of the most common types include:
- Sebaceous cysts: Smooth, round lumps caused by blocked sebaceous glands, often found on the scalp, face or torso.
- Lipomas: Soft, fatty growths that develop under the skin, usually on the shoulders, back or thighs.
- Skin tags: Small, flesh-coloured growths that often appear in areas of friction, such as the neck, armpits or groin.
- Seborrheic keratosis: Raised, waxy, and often pigmented lesions commonly associated with ageing.
- Epidermoid cysts: Small, firm bumps beneath the skin, often filled with keratin.
Why are benign skin lesions treated?
Although these lesions are not cancerous, there are several reasons why they may be treated:
- Cosmetic concerns: Many patients seek treatment to remove lesions that affect their appearance or self-confidence.
- Irritation: Lesions located in areas of friction may become inflamed, painful, or prone to bleeding.
- Diagnostic uncertainty: If a lesion's appearance raises concerns about malignancy, removal and biopsy may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
- Growth or change: Lesions that grow rapidly, change shape, or cause discomfort may warrant medical attention.
What are the different surgical approaches to benign skin lesions?
In general surgery, benign skin lesions are often removed using minimally invasive techniques. Treatment options include:
- Excisional surgery: The lesion is surgically removed, often with local anaesthesia, and sent for pathological analysis if needed.
- Curettage and cautery: The lesion is scraped off the skin, and heat is used to stop any bleeding or reduce regrowth risks.
- Cryotherapy: Small lesions may be frozen with liquid nitrogen to destroy the abnormal tissue.
Importance of general surgical care
General surgeons ensure that benign skin lesions are removed safely and with minimal risk of complications, such as infection or scarring. They also provide expert evaluation to differentiate between benign and potentially malignant lesions. Timely surgical intervention, where necessary, not only improves patient comfort but also addresses any diagnostic uncertainty, ensuring peace of mind.
Whether for aesthetic, diagnostic, or functional purposes, consulting a general surgeon for benign skin lesions is a proactive step towards maintaining skin health.


