Winning the battle against haemorrhoids: simple solutions for everyday relief
Autore:Haemorrhoids, also known as piles, are a common condition affecting many people in the UK. Although they can cause significant discomfort, there are various treatment options available, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical procedures.
This article addresses the main concerns surrounding haemorrhoids and explores practical solutions for relief.
What are haemorrhoids?
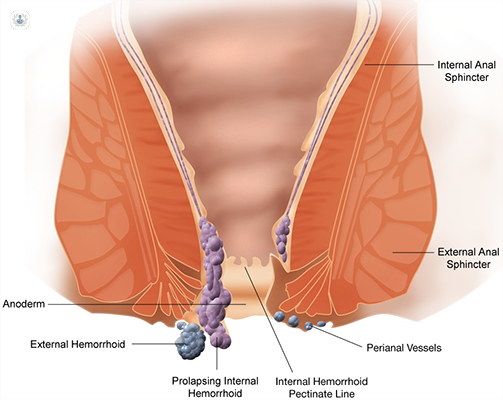
Haemorrhoids are swollen blood vessels in the rectum or anus. They can be classified as internal, which form inside the rectum, or external, which occur under the skin around the anus.
Both types can cause pain, itching, and bleeding, although external haemorrhoids are typically more painful.
What causes haemorrhoids?
Several factors can contribute to the development of haemorrhoids. These include:
- Straining during bowel movements.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhoea.
- Prolonged sitting, particularly on the toilet.
- Pregnancy, due to increased pressure on the pelvic veins.
- Obesity and a low-fibre diet.
Understanding the cause is key to both preventing and managing haemorrhoids effectively.
How can I relieve haemorrhoid symptoms at home?
For mild haemorrhoids, simple lifestyle changes and home treatments can provide significant relief:
- Increase fibre intake: Eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can soften stools and reduce straining.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps prevent constipation.
- Use over-the-counter treatments: Creams, ointments, and suppositories can help soothe itching and discomfort.
- Soak in warm baths: Sitz baths (sitting in warm water for 10-15 minutes) can ease swelling and pain.
- Avoid prolonged sitting: Regular movement reduces pressure on the rectal veins.
When should I see a doctor for haemorrhoids?
While haemorrhoids often improve with home care, it is important to consult a doctor if:
- You experience persistent or severe pain.
- There is significant bleeding, particularly if it occurs with bowel movements.
- You notice changes in bowel habits, such as chronic diarrhoea or constipation.
- Home treatments do not provide relief after a week or two.
A doctor may recommend further treatment, especially for more severe or recurrent haemorrhoids.
What medical treatments are available for haemorrhoids?
For haemorrhoids that do not respond to home treatment, several medical interventions are available:
- Rubber band ligation: A small rubber band is placed around the base of an internal haemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink.
- Sclerotherapy: A solution is injected into the haemorrhoid to shrink it.
- Infrared coagulation: A special device is used to apply heat to shrink the haemorrhoid.
- Haemorrhoidectomy: For severe cases, surgery may be required to remove the haemorrhoid.
Your doctor will help determine the best course of action based on the severity of your symptoms.
Can haemorrhoids be prevented?
Preventing haemorrhoids often involves adopting healthier bowel habits. Key strategies include:
- Eating a high-fibre diet.
- Staying well-hydrated.
- Exercising regularly to avoid constipation.
- Avoiding straining during bowel movements.
- Not delaying the urge to have a bowel movement
By making these changes, you can reduce your risk of developing haemorrhoids and minimise the likelihood of recurrence.
Conclusion
Haemorrhoids can be uncomfortable, but they are manageable with the right approach. Simple lifestyle changes, home treatments, and, if necessary, medical interventions can provide relief and prevent further issues.
If you are experiencing persistent symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice to ensure timely and appropriate treatment.


