What is an arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is also known as a heart rhythm problem, causing the heart to either beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia) or to have an irregular pattern. This results when the electrical pulses that coordinate the heartbeats do not work properly.
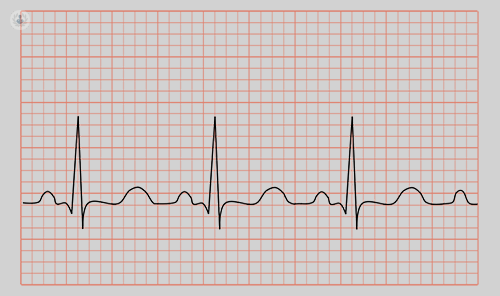
What are the symptoms of arrhythmia?
People with an arrhythmia may not experience any symptoms, but a prominent arrhythmia may result in the following symptoms:
- Palpitations
- Dizziness and vertigo
- Fainting (syncope)
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Sweating
What causes an arrhythmia?
In some cases, arrhythmias may arise in patients who do not have any other abnormalities. In other cases, arrhythmias may be secondary to other abnormalities.
Potential secondary causes include:
- Heart attack or damage to the myocardium from a heart attack in the past
- Heart failure or enlargement of the heart
- Congenital heart disease
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Abnormal levels of potassium or other substances in the body
- Smoking
- Too much caffeine or alcohol
- Stress
- Diabetes
- Genetic causes
- Recreational drug use
What is the treatment for arrhythmia?
Mild arrhythmias often won’t require treatment, but when an arrhythmia is serious treatment will be required.
Treatment can consist of:
- Medication – to control the heart beat better
- Catheter ablation – minimally-invasive procedure that destroys diseased tissue in the heart causing the arrhythmia
- Cardioversion – electric shocks are used to return the heart beat to a normal rhythm
In specific circumstances, a pacemaker or ICD (a device that monitors heart rhythm, and uses small shocks to maintain a normal rhythm), may be required.
11-13-2012 06-07-2023Arrhythmia
Dr Saagar Mahida - Cardiology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 06-07-2023
Edited by: Aoife Maguire
What is an arrhythmia?
An arrhythmia is also known as a heart rhythm problem, causing the heart to either beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia) or to have an irregular pattern. This results when the electrical pulses that coordinate the heartbeats do not work properly.

What are the symptoms of arrhythmia?
People with an arrhythmia may not experience any symptoms, but a prominent arrhythmia may result in the following symptoms:
- Palpitations
- Dizziness and vertigo
- Fainting (syncope)
- Chest pain
- Difficulty breathing
- Sweating
What causes an arrhythmia?
In some cases, arrhythmias may arise in patients who do not have any other abnormalities. In other cases, arrhythmias may be secondary to other abnormalities.
Potential secondary causes include:
- Heart attack or damage to the myocardium from a heart attack in the past
- Heart failure or enlargement of the heart
- Congenital heart disease
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Hyperthyroidism
- Abnormal levels of potassium or other substances in the body
- Smoking
- Too much caffeine or alcohol
- Stress
- Diabetes
- Genetic causes
- Recreational drug use
What is the treatment for arrhythmia?
Mild arrhythmias often won’t require treatment, but when an arrhythmia is serious treatment will be required.
Treatment can consist of:
- Medication – to control the heart beat better
- Catheter ablation – minimally-invasive procedure that destroys diseased tissue in the heart causing the arrhythmia
- Cardioversion – electric shocks are used to return the heart beat to a normal rhythm
In specific circumstances, a pacemaker or ICD (a device that monitors heart rhythm, and uses small shocks to maintain a normal rhythm), may be required.

Are ectopic heartbeats dangerous?
By Dr Boon Lim
2025-01-28
Many of us experience ectopic heartbeats without any cause for concern, but when are they considered dangerous? Dr Boon Lim explains all you need to know about these abnormal heartbeats and when to seek medical help. See more


Blackouts (syncope) explained: possible causes, diagnostic tests and when to see a doctor
By Dr Syed Afzal Sohaib
2025-01-28
About half the UK population experience syncope (a blackout) at least once in their lifetime. Usually, the cause is unrelated to the heart. However, if blackouts are caused by the heart, they usually require urgent medical attention. Mr Azfal Sohaib explains the potential causes, when to see a doctor, and the tests you might undergo. See more

When the first ablation fails: Arrhythmia after atrial (heart) ablation
By Professor Mark Gallagher
2025-01-28
If you experience arrhythmia, a doctor may recommend atrial ablation to burn and destroy the abnormal area of heart tissue that is causing the arrhythmia. While ablation will generally restore your normal heart rhythm, it is important to remember that arrhythmia may still occur after the procedure, in some cases. Here to provide a detailed insight into arrhythmia after atrial ablation, including causes, prevention and treatment, is esteemed cardiologist, Dr Mark Gallagher. See more


Can anxiety be linked to arrhythmia?
By Dr Boon Lim
2025-01-28
Dr Boon Lim is a renowned cardiologist and expert in the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias. He recently presented at the 2018 Heart Rhythm Congress in Birmingham, which is the largest meeting of heart rhythm specialists in the UK. Here he presented on several topics, including the fascinating link between arrhythmia (specifically ectopic beats) and anxiety. See more
Experts in Arrhythmia
-
Dr Fakhar Khan
CardiologyExpert in:
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Electrophysiology study
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Electrocardiogram
- Pacemaker
- Arrhythmia
-
Dr Boon Lim
CardiologyExpert in:
- Cardiac (catheter) ablation
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD)
- Arrhythmia
- Syncope
- Pacemaker
- Atrial Fibrillation
-
Dr Nick Linton
CardiologyExpert in:
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Arrhythmia
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Cardiomyopathy
- Heart attack
- Heart murmur
-
Dr Syed Ahsan
CardiologyExpert in:
- Arrhythmia
- Cardiac (catheter) ablation
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Chest pain
- Pacemaker
- Palpitations
-
Dr Martin Lowe
CardiologyExpert in:
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Palpitations
- Cardiac (catheter) ablation
- Arrhythmia
- Pacemaker
- See all

The Cavell Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
The Cavell Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Cavell Dr, Uplands Park Rd, Enfield EN2 7PR
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

The Wilmslow Hospital - part of HCA Healthcare
The Wilmslow Hospital - part of HCA Healthcare
52-54 Alderley Road, Wilmslow, Cheshire, SK9 1NY
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Goring Hall Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Goring Hall Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Bodiam Ave, Goring-by-Sea, Worthing BN12 5AT
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
The Cavell Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Cavell Dr, Uplands Park Rd, Enfield EN2 7PR, North LondonExpert in:
- endoscopy
- Gastroenterology
- Shoulder and elbow
- Hand and wrist
- Otolaryngology
- Foot and ankle
-
The Wilmslow Hospital - part of HCA Healthcare
52-54 Alderley Road, Wilmslow, Cheshire, SK9 1NY, WilmslowExpert in:
- Breast Cancer
- Men's health check
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Women’s health
- Sports Medicine
-
Goring Hall Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Bodiam Ave, Goring-by-Sea, Worthing BN12 5AT, Goring-by-SeaExpert in:
- Hip
- Cataracts
- Gallbladder surgery
- General Surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Hernia
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Respiratory infection
- Osteoporosis
- Narcolepsy
- Snoring
- Polysomnography (sleep study)
- Alzheimer's disease
- Chronic headache
- Electrophysiology study
- Autoimmune diseases
- Joint pain








