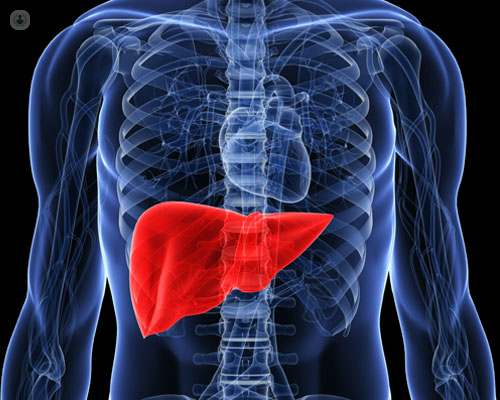
What is fatty liver?
Fatty liver disease is the accumulation of fatty acids and triglycerides in liver cells. There are two types:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: it is the most common cause for obesity due to a build-up of fat in the liver cells. There are other factors that can also trigger the disease, such as oxidative stress, the production and release of toxic inflammatory proteins, or necrosis or death of liver cells.
- Alcohol-related liver disease, also known as alcohol hepatic steatosis: as the name suggests, this disease is caused by excess alcohol intake. The liver breaks down most of the alcohol but during the process, harmful substances to the liver are released that cause inflammation and weaken the body’s natural defences.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of this disease include upper right abdominal pain, general malaise, and chronic fatigue, among others. However, many patients don’t have symptoms but are diagnosed after having certain imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan for other reasons.
These imaging tests are not always able to diagnose this disease, for this it’s best to undergo laboratory testing to be able to assess the degree of liver injury by assessing liver enzymes or transaminases.
Causes of fatty liver?
Specialists are still unsure as to why some people accumulate fat in the liver and others don’t. An important factor is that some cases of fatty liver develop swelling which could turn into cirrhosis. There are however some common factors for both types of fatty liver: being overweight or obese, insulin resistance, when cells don’t process sugar in response to the hormone insulin, and high blood sugar levels (hyperglycaemia) which can indicate prediabetes or type 2 diabetes and / or high levels of blood fats, particularly triglycerides.
How can it be prevented?
In most cases, fatty liver can be prevented if certain lifestyle changes are made, such as following healthy guidelines based on a varied, balanced, and low fat diet. Since alcohol is one of the things that damages the liver, it is very important to stop consuming alcohol.
Another important factor is to exercise regularly as that helps burn fat; exercises can be aerobic, such as running or walking.
What is the treatment?
There is no specific treatment for this disease, however it has been shown that weight loss, regular exercise, and following a balanced diet can help reduce fat in the liver.
Controlling cholesterol levels, diabetes, and / or any other cause for a build-up of fat in the liver is also important.
In cases of morbid obesity, bariatric surgery may be recommended.
11-13-2012 02-07-2024Fatty liver
Professor Kevin Peter Moore - Hepatology (liver specialist)
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 02-07-2024
What is fatty liver?
Fatty liver disease is the accumulation of fatty acids and triglycerides in liver cells. There are two types:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: it is the most common cause for obesity due to a build-up of fat in the liver cells. There are other factors that can also trigger the disease, such as oxidative stress, the production and release of toxic inflammatory proteins, or necrosis or death of liver cells.
- Alcohol-related liver disease, also known as alcohol hepatic steatosis: as the name suggests, this disease is caused by excess alcohol intake. The liver breaks down most of the alcohol but during the process, harmful substances to the liver are released that cause inflammation and weaken the body’s natural defences.

What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of this disease include upper right abdominal pain, general malaise, and chronic fatigue, among others. However, many patients don’t have symptoms but are diagnosed after having certain imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan for other reasons.
These imaging tests are not always able to diagnose this disease, for this it’s best to undergo laboratory testing to be able to assess the degree of liver injury by assessing liver enzymes or transaminases.
Causes of fatty liver?
Specialists are still unsure as to why some people accumulate fat in the liver and others don’t. An important factor is that some cases of fatty liver develop swelling which could turn into cirrhosis. There are however some common factors for both types of fatty liver: being overweight or obese, insulin resistance, when cells don’t process sugar in response to the hormone insulin, and high blood sugar levels (hyperglycaemia) which can indicate prediabetes or type 2 diabetes and / or high levels of blood fats, particularly triglycerides.
How can it be prevented?
In most cases, fatty liver can be prevented if certain lifestyle changes are made, such as following healthy guidelines based on a varied, balanced, and low fat diet. Since alcohol is one of the things that damages the liver, it is very important to stop consuming alcohol.
Another important factor is to exercise regularly as that helps burn fat; exercises can be aerobic, such as running or walking.
What is the treatment?
There is no specific treatment for this disease, however it has been shown that weight loss, regular exercise, and following a balanced diet can help reduce fat in the liver.
Controlling cholesterol levels, diabetes, and / or any other cause for a build-up of fat in the liver is also important.
In cases of morbid obesity, bariatric surgery may be recommended.

Why see a hepatologist (liver specialist)?
By Professor Kevin Peter Moore
2024-12-15
The liver is estimated to perform 500+ vital functions in the body. If your doctor suspects you may be having a problem with your liver, they may refer you to a specialist called a hepatologist. Professor Kevin Moore explains what a liver specialist does, & the kinds of patient he is able to see. See more


Liver disease: can the liver repair itself after years of drinking?
By Dr Ghazanfar Ali
2024-12-15
Alcohol is frequently used to add to the enjoyment of life, but it does come with some negative consequences, one of these being alcohol related liver disease (ARLD). Mr Ghazanfar Ali is a leading gastroenterologist with many years of experience in treating liver disease and here he provides answers to the most common questions. See more


What is a FibroScan and why would I need one?
By Professor Kevin Peter Moore
2024-12-15
A fibroScan is a type of ultrasound which measures how much scarring there is in your liver due to liver disease. It is quick, painless and frequently obviates the need for a liver biopsy. See more


Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: give your liver a gift this Christmas
By Dr Jeremy Cobbold
2024-12-14
It's been a tough year for everyone, and while the urge to overindulge in mince pies and Christmas pudding this year might be much harder to resist, Dr Jeremy Cobbold - a consultant hepatologist and gastroenterologist - reminds us of how we can continue to enjoy our festive treats without going down the road to an unhealthy liver. See more
Experts in Fatty liver
-
Professor Kevin Peter Moore
Hepatology (liver specialist)Expert in:
- Ascites
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Cirrhosis
- Fatty liver
- Haemochromatosis
- Alcoholism
-
Professor Patrick Kennedy
Hepatology (liver specialist)Expert in:
- Liver disease
- Liver function tests
- Viral hepatitis
- Fatty liver
- Alcoholism
- Abdominal pain
-
Professor Raj Mookerjee
GastroenterologyExpert in:
- Cirrhosis
- Fatty liver
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Endoscopy
- Biopsy
-
Professor Daniel Forton
GastroenterologyExpert in:
- Abdominal pain
- Endoscopy
- Fatty liver
- FibroScan
- Liver disease
- Viral hepatitis
-
Dr Andrew Peter Holt
Hepatology (liver specialist)Expert in:
- Cirrhosis
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Fatty liver
- Viral hepatitis
- Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)
- Liver transplant
- See all

The Harley Street Clinic - part of HCA Healthcare
The Harley Street Clinic - part of HCA Healthcare
35 Weymouth Street, London. W1G 8BJ
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

LycaHealth Canary Wharf
LycaHealth Canary Wharf
1 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf. E14 4HD
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

The Royal Free Hospital
The Royal Free Hospital
Pond Street, Hampstead. NW3 2QG
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
The Harley Street Clinic - part of HCA Healthcare
35 Weymouth Street, London. W1G 8BJ, Central LondonExpert in:
- Cancer
- Head and neck cancer
- Cardiology
- Intensive care
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Women’s health
-
LycaHealth Canary Wharf
1 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf. E14 4HD, Central LondonExpert in:
- Cardiology
- Dermatology
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Women’s health
-
The Royal Free Hospital
Pond Street, Hampstead. NW3 2QG, Central LondonExpert in:
- General Surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Robotic Surgery
- Dermatology
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Paediatrics
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Electrophysiology study
- Autoimmune diseases
- Joint pain
- Nutrition
- Weight loss injections
- Endermologie
- Genetic testing
- Abdominal pain
- Vaginal cytology
- Parkinson's disease







