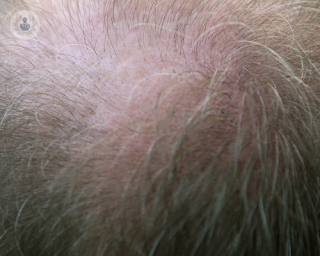
What is hair loss?
Hair loss, to an extent, is normal and we lose up to 100 strands of hair a day, usually without noticing. There are different types of hair loss, some are permanent, whilst others are temporary. Hair loss can also be hereditary, such as male and female pattern baldness. Dermatologists usually treat patients with hair loss.
There are other types of hair loss, also called alopecia, including:
- Alopecia areata (AA) – a very common form of hair loss, causing patchy hair loss, sometimes leading to total hair loss.
- Involutional alopecia – natural thinning of the hair with age.
- Androgenic alopecia – is male and female pattern baldness. Often this starts in the 20s in men, and the 40s or later in women.
- Alopecia universalis – total hair loss from all over the body (including facial and pubic hair).
- Trichotillomania – a psychological disorder, common in children, characterised by the pulling out of one’s own hair.
- Traction alopecia – hair loss caused by having the hair styled in tight braids.
- Scarring alopecia – skin conditions, such as acne and cellulitis, can cause scarring which destroys the hair’s ability to regenerate. What is the prognosis of hair loss?
What are the symptoms of hair loss?
The signs of hair loss can differ between men and women, but commonly, you might notice more hair than usual collecting in the plug hole of your shower, and in your hair brush.
Hair loss in men can happen in the following ways:
- A receding hair line
- Thinning hair over the scalp
- A horseshoe shape is exposed, leaving the crown of the head bald.
Hair loss in women is usually more of a gradual, all-over thinning, concentrated on the crown of the head.
How is hair loss diagnosed?
When visiting your doctor for hair loss, they will first complete a physical examination and ask you about your medical and family history. The following may also be carried out to determine the cause of your hair loss:
- A blood test
- Light microscopy – a special instrument examines hair at their base.
- Scalp biopsy – skin samples are tested.
What are the causes of hair loss?
Whilst some forms of hair loss are hereditary, others can be caused by:
- An illness
- Medical treatments, such as chemotherapy
- Weight loss
- Hormone changes
- Skin conditions (e.g. infection)
- Mental health (e.g. stress)
Can hair loss be prevented?
Certain types of hair loss cannot be prevented, but there are steps you can take to take better care of your hair, such as avoiding tightly pulled back hair styles, avoiding stiff hair curlers, brushing your hair gently and not pulling through tangles.
How is hair loss treated?
Some forms of hair loss are temporary, and with time, the hair will grow back. Such cases do not require treatment. Other forms of hair loss are part of the natural ageing process, and also won’t need treatment.
There are certain medications that can be taken to treat male and female pattern baldness. These include Finasteride and Minoxidil. However, these can be costly, not always effective and include some side-effects.
Other treatments include:
- Hair transplant surgery
- Steroid injections
- Steroid creams
- Light treatment (UV light applied to bald patches)
- Tattooing can help disguise hair loss on the eyebrows
- Wigs
Which type of specialist treats hair loss?
The different specialists that might diagnose or treat hair loss include aesthetic medicine specialists, plastic surgeons, psychiatrists and oncologists.
07-30-2018 11-28-2023Hair loss
Dr Ophelia Veraitch - Dermatology
Created on: 07-30-2018
Updated on: 11-28-2023
Edited by: Sophie Kennedy
What is hair loss?
Hair loss, to an extent, is normal and we lose up to 100 strands of hair a day, usually without noticing. There are different types of hair loss, some are permanent, whilst others are temporary. Hair loss can also be hereditary, such as male and female pattern baldness. Dermatologists usually treat patients with hair loss.
There are other types of hair loss, also called alopecia, including:
- Alopecia areata (AA) – a very common form of hair loss, causing patchy hair loss, sometimes leading to total hair loss.
- Involutional alopecia – natural thinning of the hair with age.
- Androgenic alopecia – is male and female pattern baldness. Often this starts in the 20s in men, and the 40s or later in women.
- Alopecia universalis – total hair loss from all over the body (including facial and pubic hair).
- Trichotillomania – a psychological disorder, common in children, characterised by the pulling out of one’s own hair.
- Traction alopecia – hair loss caused by having the hair styled in tight braids.
- Scarring alopecia – skin conditions, such as acne and cellulitis, can cause scarring which destroys the hair’s ability to regenerate. What is the prognosis of hair loss?
What are the symptoms of hair loss?
The signs of hair loss can differ between men and women, but commonly, you might notice more hair than usual collecting in the plug hole of your shower, and in your hair brush.
Hair loss in men can happen in the following ways:
- A receding hair line
- Thinning hair over the scalp
- A horseshoe shape is exposed, leaving the crown of the head bald.
Hair loss in women is usually more of a gradual, all-over thinning, concentrated on the crown of the head.
How is hair loss diagnosed?
When visiting your doctor for hair loss, they will first complete a physical examination and ask you about your medical and family history. The following may also be carried out to determine the cause of your hair loss:
- A blood test
- Light microscopy – a special instrument examines hair at their base.
- Scalp biopsy – skin samples are tested.
What are the causes of hair loss?
Whilst some forms of hair loss are hereditary, others can be caused by:
- An illness
- Medical treatments, such as chemotherapy
- Weight loss
- Hormone changes
- Skin conditions (e.g. infection)
- Mental health (e.g. stress)
Can hair loss be prevented?
Certain types of hair loss cannot be prevented, but there are steps you can take to take better care of your hair, such as avoiding tightly pulled back hair styles, avoiding stiff hair curlers, brushing your hair gently and not pulling through tangles.
How is hair loss treated?
Some forms of hair loss are temporary, and with time, the hair will grow back. Such cases do not require treatment. Other forms of hair loss are part of the natural ageing process, and also won’t need treatment.
There are certain medications that can be taken to treat male and female pattern baldness. These include Finasteride and Minoxidil. However, these can be costly, not always effective and include some side-effects.
Other treatments include:
- Hair transplant surgery
- Steroid injections
- Steroid creams
- Light treatment (UV light applied to bald patches)
- Tattooing can help disguise hair loss on the eyebrows
- Wigs
Which type of specialist treats hair loss?
The different specialists that might diagnose or treat hair loss include aesthetic medicine specialists, plastic surgeons, psychiatrists and oncologists.

Exosome treatment: Understanding its benefits and results
By Dr Jacqueline Lewis
2024-12-15
Exosome treatment is an advanced form of regenerative therapy that utilises exosomes, which are small extracellular vesicles released by cells, particularly stem cells. See more


Male pattern hair loss (MPHL) and male pattern baldness (MPB)
By Dr Aleksandar Godic
2024-12-15
Losing your hair can be a distressing experience and there is an abundance of urban myths surrounding male-pattern baldness. Leading consultant dermatologist Dr Aleksander Godic helps to establish the facts in this article on the most common causes of hair loss in men. See more

Telogen effluvium: why is my hair falling out?
By Dr Aleksandar Godic
2024-12-15
Telogen effluvium or diffuse hair loss can strike at any time, causing the sufferer to suddenly experience thinning hair. See more


The role of genetics in determining hair colour
By Dr Nilofer Farjo
2024-12-15
Hair colour is well-known to be an inherited trait from our parents. However, did you know that there's more to it than just 'dominant' and 'submissive' genes? Here to provide a detailed look at hair colour and genetics, is respected hair transplant specialist Dr Nilofer Farjo. See more
Experts in Hair loss
-
-
-
-
Dr Anne Farrell
DermatologyExpert in:
- Acne
- Moles
- Laser
- Paediatric dermatology
- Hair loss
- Photodynamic therapy
-
Dr Amandeep Singh Grewal
GP (general practitioner)Expert in:
- Allergy
- Acne
- Men's health check
- Health check up (health screening)
- Hair loss
- Cosmetic dermatology
- See all

The Hair Dr
The Hair Dr
78 Bradford Road
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Skin Inspection Dermatology Clinic
Skin Inspection Dermatology Clinic
Harley Street Clinic 55 Harley Street 4th Floor, London
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Derma Reading
Derma Reading
Shepherds Hill, Woodley, RG6 1FE
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
The Hair Dr
78 Bradford Road, DewsburyExpert in:
- Hair transplant surgery
- Plastic surgery, reconstructive and aesthetics
- Hair restoration
- FUE hair transplant
-
Skin Inspection Dermatology Clinic
Harley Street Clinic 55 Harley Street 4th Floor, London, W1G Marylebone LondonExpert in:
- Skin Cancer
- Clinical Dermatology
- Surgical Dermatology
- Diagnosis of Cancer
- Moles
- Cancer Treatment
-
Derma Reading
Shepherds Hill, Woodley, RG6 1FE, ReadingExpert in:
- Acne
- Skin Cancer
- Paediatric Dermatology
- Moles
- Aesthetic Medicine
- Hair loss
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Facial feminisation surgery
- Hormone therapy
- Migraine
- Autoimmune diseases
- Joint pain
- Nutrition
- Weight loss injections
- Endermologie
- Polynucleotides
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLA)









