What is a stress test?
A stress test (also known as the cardiac stress test, exercise ECG or exercise stress test) is used to diagnose and assess the blood flow within your heart. It diagnoses coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) and it guides treatment decisions for other heart conditions.
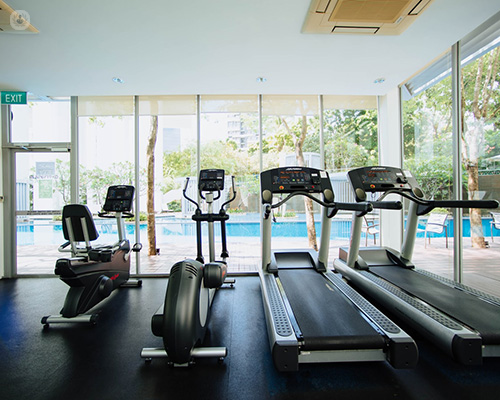

What happens during the stress test?
During a stress test, you will walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary exercise bike. Exercise makes the heart pump harder and faster and can reveal any blood flow problems. The stress test normally takes around one hour, which includes prep time and the time it takes to perform the actual test. The exercise part of the stress test takes around 15 minutes.
How do I prepare for the stress test?
Before the patient undergoes a stress test, the specialist will take a medical history from the patient. The doctor will take your weight, height and body mass index (BMI) as well as measuring your fat, bone and muscle percentage.
A nurse will place sticky patches (electrodes) on your chest, legs and arms. The electrodes have wires that are connected to an electrocardiogram machine and records the electrical signals that trigger your heartbeats. As the stress test progresses, that exercise becomes more difficult. The doctor will be looking out for particular symptoms or signs of heart problems.
What can occur during a stress test?
During a stress test, you will exercise until your heart rate has reached a set target or until you develop symptoms such as:
- Moderate to severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Abnormally low or high blood pressure
- Feeling dizzy
- Fatigue
How do you feel during the exam?
The patient will wear electrodes on the chest to record the activity of the heart. These can cause a burning sensation or mild itching. Although the stress test is generally safe, it can rarely cause chest pain or fainting in some people.
What do the results of a stress test mean?
If stress test results show the heart function is normal, no further tests are required. If the stress test results are abnormal, however, your doctor may recommend a nuclear stress test or another type of stress test, which includes an echocardiogram before and after exercise. These tests are more accurate and will provide more information about your heart.
The stress test may highlight if you have coronary artery disease or arrhythmia and your doctor will develop a treatment plan.
Stress test
Dr Francesco Lo Monaco - Cardiology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 05-09-2023
Edited by: Karolyn Judge
What is a stress test?
A stress test (also known as the cardiac stress test, exercise ECG or exercise stress test) is used to diagnose and assess the blood flow within your heart. It diagnoses coronary artery disease, heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) and it guides treatment decisions for other heart conditions.

What happens during the stress test?
During a stress test, you will walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary exercise bike. Exercise makes the heart pump harder and faster and can reveal any blood flow problems. The stress test normally takes around one hour, which includes prep time and the time it takes to perform the actual test. The exercise part of the stress test takes around 15 minutes.
How do I prepare for the stress test?
Before the patient undergoes a stress test, the specialist will take a medical history from the patient. The doctor will take your weight, height and body mass index (BMI) as well as measuring your fat, bone and muscle percentage.
A nurse will place sticky patches (electrodes) on your chest, legs and arms. The electrodes have wires that are connected to an electrocardiogram machine and records the electrical signals that trigger your heartbeats. As the stress test progresses, that exercise becomes more difficult. The doctor will be looking out for particular symptoms or signs of heart problems.
What can occur during a stress test?
During a stress test, you will exercise until your heart rate has reached a set target or until you develop symptoms such as:
- Moderate to severe chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Abnormally low or high blood pressure
- Feeling dizzy
- Fatigue
How do you feel during the exam?
The patient will wear electrodes on the chest to record the activity of the heart. These can cause a burning sensation or mild itching. Although the stress test is generally safe, it can rarely cause chest pain or fainting in some people.
What do the results of a stress test mean?
If stress test results show the heart function is normal, no further tests are required. If the stress test results are abnormal, however, your doctor may recommend a nuclear stress test or another type of stress test, which includes an echocardiogram before and after exercise. These tests are more accurate and will provide more information about your heart.
The stress test may highlight if you have coronary artery disease or arrhythmia and your doctor will develop a treatment plan.


Exercise testing: how strong is your heart?
By Dr Sukhjinder Nijjer
2025-01-28
An exercise test, also known as a stress test, evaluates how well your heart can cope with physical exertion. You may need this done for a medical test for work or perhaps your heart has shown irregularities. Dr Sukhjinder Nijjer regularly performs this test and in this article, he explains all you need about this test and how to prepare. See more


How cardiologists help professional and recreational athletes train safely
By Dr Sabiha Gati
2025-01-28
Cardiologists help all levels of athletes train safely, no matter what their level is. Learn from Dr Sabiha Gati, a leading UK cardiologist, about how you can benefit from cardiac screening and what to expect during a sports cardiology consultation. See more


Exercise stress test: what does it detect?
By Dr Sabiha Gati
2025-01-28
An exercise test is used to determine how your heart responds when it's working at full strength and can reveal any problems related to your heart rate and blood pressure during exercise. Wondering what to expect on the day? Read more from one of London's leading cardiologists Dr Sabiha Gati. See more

Understanding non-invasive tests for cardiological chest pain
By Dr Gosia Wamil
2025-01-28
If you've ever experienced chest pain, you know how worrying it can be. Thankfully, there are several non-invasive tests that doctors use to get a clear picture of your heart and help determine what's causing the pain. Here’s a simple guide to three common tests your cardiologist might recommend. See more
Experts in Stress test
-
Dr Francesco Lo Monaco
CardiologyExpert in:
- Echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- Heart check up
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Palpitations
- Stress test
-
Dr Sabiha Gati
CardiologyExpert in:
- Sports cardiology
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiac screening
- Cardiac MRI
- Echocardiogram
- Stress test
-
Dr Vinay Kumar Bhatia
CardiologyExpert in:
- Echocardiogram
- Stress test
- Transoesophageal echocardiogram
- Heart failure
- Coronary heart disease
- Arrhythmia
-
Dr Jakub Lagan
CardiologyExpert in:
- Stress test
- Cardiac MRI
- Echocardiogram
- Transoesophageal echocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram
- Coronary CT
-
Dr Sothinathan (Nathan) Gurunathan
CardiologyExpert in:
- Cardio-oncology
- Stress test
- Heart check up
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Palpitations
- Chest pain
- See all

Cleveland Clinic London Hospital
Cleveland Clinic London Hospital
33 Grosvenor Place, SW1X 7HY
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Syon Clinic - part of Circle Health Group
Syon Clinic - part of Circle Health Group
941 Great West Rd, Brentford TW8 9DU
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Private Care at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital
Private Care at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital
Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, 369 Fulham Rd.
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
Cleveland Clinic London Hospital
33 Grosvenor Place, SW1X 7HY, Central LondonExpert in:
- Cardiology
- Colorectal surgery
- Minimal access surgery (keyhole surgery)
- Gallbladder surgery
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Ultrasound
-
Syon Clinic - part of Circle Health Group
941 Great West Rd, Brentford TW8 9DU, West LondonExpert in:
- Allergies nose and ears
- Allergy Dermatitis
- Allergy
- Clinical analysis
- Anxiety
- Digestive
-
Private Care at Chelsea and Westminster Hospital
Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, 369 Fulham Rd., Central LondonExpert in:
- General Surgery
- Dermatology
- Paediatric Dermatology
- Paediatrics
- Preventive paediatrics
- Adult and paediatric services
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Electrophysiology study
- Joint pain
- Genetic testing
- Anxiety
- Long Covid
- Botulinum toxin (Botox™)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Back pain
- Platelet-rich plasma
- Medicolegal







