Thyroid nodules
Miss Aimee Di Marco - Surgery
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 11-02-2023
Edited by: Karolyn Judge
What are thyroid nodules?
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths of thyroid cells and tissue which form a lump in the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the neck and releases thyroid hormone, which helps to control the body’s metabolism.
Thyroid nodules are usually non-cancerous (benign), but some are cancerous, which means thyroid nodules must be evaluated in order to treat thyroid cancer in its early stages.
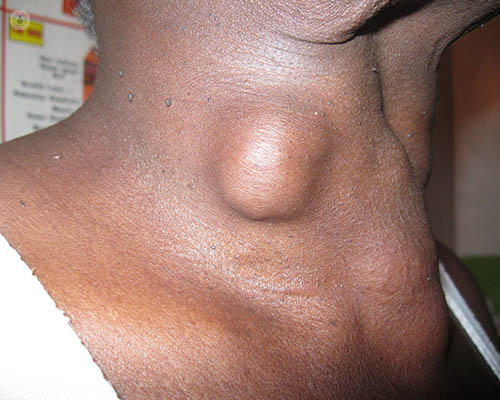
What are the symptoms?
Thyroid nodules usually do not cause symptoms, and most are found during routine examinations or through CT scans or other similar imaging tests. Most thyroid nodules are non-functioning, but some do produce an excess of thyroid hormone, which results in hyperthyroidism. Thyroid nodules may become noticeable if the nodule is large enough, as a lump may be seen on the neck, or the nodule may cause problems breathing and swallowing due to it restricting the windpipe.
What causes thyroid nodules?
Thyroid nodules don't always have a known or apparent cause. Some nodules are associated with iodine deficiency, but this is uncommon as iodine is often added to salt and other foods. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition, is associated with an increased risk of developing thyroid nodules. Thyroid nodules can be caused by an excess of thyroid tissue, swelling of the thyroid (goitre), and thyroid cysts. However, it is not always clear why growths and swelling occur.
How can they be prevented?
Thyroid nodules cannot be prevented. There are tests which can determine if an individual has a thyroid nodule, but these should always be discussed with a doctor.
How are thyroid nodules treated?
Treatment for thyroid nodules depends on whether the nodule is benign or cancerous, and if it is functioning or not.
If a thyroid nodule is cancerous, it must be removed surgically. Thyroid cancer, on the whole, is treatable and curable. Surgery may also be performed if the thyroid nodule is particularly large and causes the patient discomfort. The nodule also may be removed if it is actively secreting hormones.
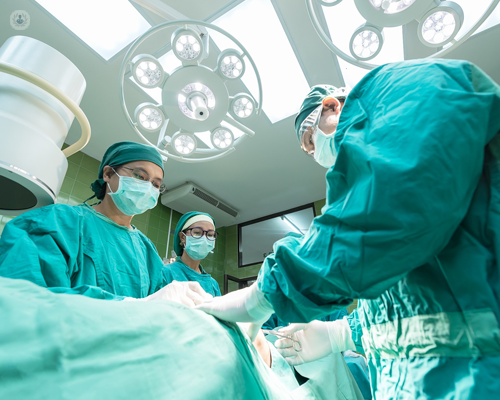
If a thyroid nodule is benign, then treatment may not be necessary, and the thyroid nodule will be monitored closely. Thyroid function tests and physical examinations will be performed regularly to make sure the nodule is still benign. If the thyroid nodule produces thyroid hormones, this can be treated using medication, radioactive iodine treatment, or in some cases, surgery.