Hip pain: How do you know if you have a labral tear?
Escrito por:A labral tear is a common injury affecting football and rugby players. In some cases, rest and changes to your physical activity will improve the symptoms, but sometimes you might need surgery. In this article, skilled consultant trauma and orthopaedic surgeon Mr Rishi Chana explains what a labral tear is, what symptoms to watch out for, and how it can be treated.

What is a labral tear?
Hip and groin injuries often affect football and rugby players as well as athletes taking part in running sports such as marathons and triathalons. The risks come from the repetitive fast changes in pace of running and a quick change of direction when twisting or pivoting in tackling.
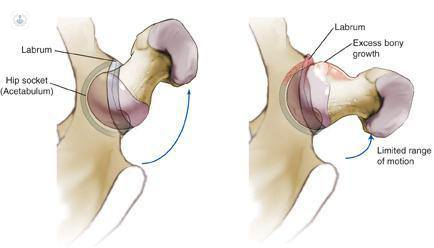
A labral tear occurs inside the hip joint and involves the labral cartilage layer. This is a flexible, rubber-like lip at the edge of socket of the hip.
The hip is a ball and socket joint. The labral lip seals the joint for better fluid lubrication. A tear occurs because of a hard tackle or a kick when the joint is in a stressed position.
Sometimes the ball of the hip is not completely round but more egg shaped. This extra bony bump can jam up against the round socket, causing a labral tear and pain. This is known as CAM impingement.
What are symptoms?
When you have a labral tear, it can feel like the hip is coming out of the socket and clicking can often be felt when moving the joint. Other symptoms include:
- groin pain in the front skin crease
- discomfort around the outer part of the hip and buttock area.
- pain when putting on shoes or socks or getting in and out of a car
- worsening pain when lifting the knee and twisting
What diagnostics are required? What technology is used?
A good clinical examination is always important.
As for scanning, plain X-rays are helpful but an MRI scan is the gold standard to show whether a labral tear has occurred. This will also detect if the ball has an extra bump of bone or whether the socket has any problems.
What treatment is required?
Rest and anti-inflammatories will alleviate the immediate pain. Activity modification and physiotherapy will also improve things further but if symptoms continue then an orthopaedic opinion will be required.
An injection can help to get rid of the pain to allow rehabilitation, but if the problem comes back despite best efforts, an operation should be considered.
What will the surgery involve?
The operation will aim to repair the tear and remove the extra bony bump. This has good results in relief from the pain, and will stop the ball and socket joint from jamming up, preventing further damage to the joint cartilage.
How long will it take to recover?
Rehabilitation after surgery starts with 2 to 4 weeks protected weight-bearing. Strengthening exercises take place at 6 to 8 weeks. On average, you’ll be able to return to sport after 12 weeks.
If you have an ongoing symptoms of a sports injury which you’d like to have investigated, book a consultation with Mr Rishi Chana today.



