The use of Botox™ in ophthalmology
Written by:While Botox™ is widely recognised for its cosmetic benefits, it also has significant medical uses, particularly in the field of ophthalmology. Originally developed to treat eye conditions, Botox™ continues to be an essential tool for ophthalmologists in managing various ocular and neurological disorders.
Leading consultant ophthalmic and oculoplastic surgeon Mr Nikhil Cascone tells us all about how Botox™ has proven to be an effective method of treatment in ophthalmology.
What is Botox™?
Botox™ is a purified form of botulinum toxin type A, a neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Botox™, when injected in small, controlled doses, temporarily relaxes muscles by blocking the release of acetylcholine. This is a neurotransmitter that’s responsible for muscle contraction.
What eye conditions can be treated with Botox™?
Botox™ is used to treat several eye and neurological conditions, including:
- Strabismus (Squint): A condition where the eyes don’t align properly, causing one eye to turn in a different direction.
- Blepharospasm: Involuntary, repetitive blinking or eyelid spasms.
- Hemifacial spasm: Involuntary muscle contractions on one side of the face.
- Chronic migraine: Botox™ can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines, which often present with ocular symptoms.
How does Botox™ help with strabismus?
Strabismus occurs when there is an imbalance in the muscles that control eye movement. Botox™ can be injected into specific eye muscles to temporarily weaken them, allowing the opposing muscles to strengthen and realign the eyes. This treatment can help improve eye alignment and coordination.
How is Botox™ used for blepharospasm?
In patients with blepharospasm, Botox™ is injected into the muscles around the eyes to reduce involuntary contractions. This treatment helps alleviate symptoms such as excessive blinking and eyelid closure, improving the patient’s ability to see and perform daily activities.
How effective is Botox™ for hemifacial spasm?
Hemifacial spasm is where one side of the face experiences involuntary twitching or muscle contractions. It often starts around the eye. Botox™ injections can relax the affected muscles, providing significant relief from spasms and improving facial symmetry.
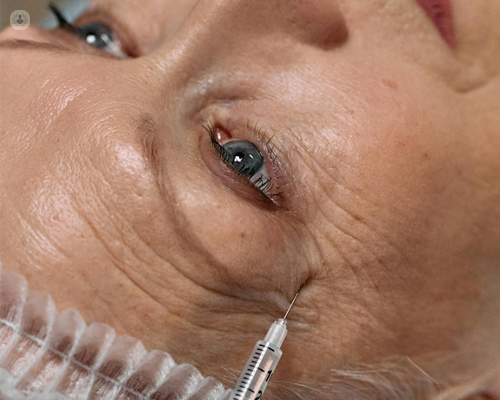
What is the procedure for administering Botox™?
The procedure for administering Botox™ in ophthalmology involves several steps:
Consultation
An ophthalmologist will assess the patient’s condition and determine if Botox™ is an appropriate treatment option.
Preparation
The injection site is cleaned, and a local anaesthetic may be applied to minimise discomfort.
Injection
Using a fine needle, the ophthalmologist injects Botox™ into the targeted muscles. The number and location of injections depend on the specific condition being treated.
Aftercare
Patients are advised to avoid rubbing the injection site and to follow any specific post-procedure instructions provided by the doctor.
What are the benefits of Botox™ in ophthalmology?
Botox™ offers several benefits in the treatment of eye conditions:
- Minimally invasive: The injections are relatively quick and do not require surgery.
- Temporary effects: The muscle relaxation effects last for several months, allowing for adjustments in treatment as needed.
- Improved quality of life: Reducing symptoms such as misalignment, spasms, and excessive blinking can significantly enhance a patient’s daily functioning and comfort.
Are there any side effects or risks?
As with any medical treatment, there are potential side effects and risks associated with Botox™ injections:
- Mild discomfort: Some patients may experience slight pain or bruising at the injection site.
- Temporary weakness: In rare cases, adjacent muscles may be temporarily weakened, potentially affecting eyelid function or facial expression.
- Allergic reactions: Although uncommon, allergic reactions to Botox™ can occur.
Patients should discuss potential risks and side effects with their ophthalmologist before undergoing treatment.
Botox™ has proven to be a versatile and effective treatment for various ophthalmic conditions, offering significant relief for patients. By understanding its applications and benefits, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options and improve their quality of life under the guidance of a qualified ophthalmologist.
Do you require treatment for an eye consultation that could involve Botox™ ? Arrange a consultation with Mr Cascone via his Top Doctors profile.


