Understanding diabetic retinopathy: A comprehensive guide for patients
Written in association with:Diabetic retinopathy is a significant concern for individuals living with diabetes, as it poses a potential threat to vision. In this article, leading consultant ophthalmic surgeon Dr Ashraf Khan explores the basics of diabetic retinopathy, including the causes, prevention strategies, and available treatment options.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, it can lead to damage of the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina, causing them to weaken, leak, or become blocked. This, in turn, can result in vision problems.
Types of diabetic retinopathy
There are two primary types of diabetic retinopathy:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR): In NPDR, in the early stage, small blood vessels in the retina weaken and leak. This may lead to mild vision problems.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR): PDR is more severe. It occurs when new, abnormal blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina, potentially causing bleeding into the eye and leading to severe vision loss.
Prevention strategies
- Maintain good blood sugar control: Keeping your blood sugar levels within the recommended range is the most crucial step in preventing diabetic retinopathy.
- Regular eye exams: Schedule regular eye examinations with your optometrist or ophthalmologist. Early detection and intervention are key to managing this condition.
- Blood pressure control: High blood pressure can exacerbate diabetic retinopathy. Maintain a healthy blood pressure through lifestyle changes or prescribed medications.
- Cholesterol management: Keeping cholesterol levels in check is essential to reduce the risk of eye complications.
- Healthy lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can improve overall health and decrease the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
Well-controlled diabetes and diabetic retinopathy
It's a common misconception that well-controlled diabetes eliminates the risk of diabetic retinopathy. While good blood sugar management significantly reduces the risk, other factors like genetics and the duration of diabetes also play a role. Regular eye exams are crucial even if your diabetes is well-managed, as early signs may still appear.
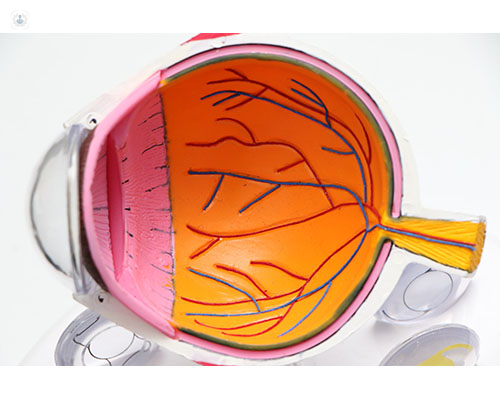
Treatment options
Several treatment options are available to manage diabetic retinopathy:
- Laser therapy (Photocoagulation): This procedure seals off leaking blood vessels and reduces the growth of abnormal ones.
- Intravitreal injections: Medications are injected into the vitreous (gel-like substance in the eye) to reduce swelling and block abnormal vessel growth.
- Vitrectomy: In advanced cases, vitrectomy may be necessary to remove blood and scar tissue from the eye.
- Anti-VEGF injections: These injections help reduce the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina.
- Regular monitoring: Close monitoring of your eye health and continued management of your diabetes is crucial in the long term.
In conclusion, diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that affects the eyes of individuals living with diabetes. Regular check-ups, good blood sugar control, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk. However, it's important to remember that even with excellent diabetes management, the risk may still exist. Early detection through regular eye exams and prompt treatment can help preserve your vision. If you have any concerns or questions about diabetic retinopathy, don't hesitate to reach out to your ophthalmologist or eye specialist. Your eyesight is a valuable asset, and protecting it is of utmost importance.
If you would like to book a consultation with Dr Ashraf Khan you can do so today via his Top Doctors profile.


