What are the different kinds of non-invasive cardiac imaging tests?
Written in association with:Non-invasive cardiac imaging is the collective term for a number of methods used to obtain images of the heart structures and function, allowing the specialist to identify potential problems with the heart, possible heart conditions, and to monitor existing heart conditions. Non-invasive cardiac imaging is relatively safe and easy to perform, leading to faster diagnosis in many situations. Leading consultant cardiologist, Dr Yousef Daryani talks through the different methods available, and how they differ from each other.

When is cardiac imaging used?
Cardiac imaging is usually used for one of three reasons: to identify heart disease based on a patient’s symptoms; to identify the risk of developing heart disease in the future; and to make decisions on what necessary treatments and procedures may be needed, such as in patients with coronary artery disease or valvular heart disease.
What are the different kinds of non-invasive cardiac imaging?
There are a number of different methods of cardiac imaging available, with different tests used to identify different conditions. Sometimes these tests complement each other but one may better suit the individual patient to start with. Sometimes it is a matter of patient choice after discussing the pros and cons of each test. The specialist will make the decision on the best cardiac imaging method based on the patient's symptoms.
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram, otherwise known simply as ‘echo’, is an ultrasound test that monitors the pumping function of the heart, and how the heart valves are functioning. This gives the doctor information about the size of the heart’s chambers, the thickness of the heart muscle, and to check for fluid around the lining of the heart. It is most commonly used to check that the heart is pumping properly, to identify if there is heart disease in the valves, and to check for damage following a heart attack.
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, or cardiac MRI for short, is a test used to evaluate the many forms of heart disease such as heart muscle dysfunction (in cases of  heart failure and cardiomyopathy), coronary artery disease and heart muscle viability (with perfusion and stress testing), masses in the heart, and rare cardiac conditions. If a stress perfusion MRI test is considered patients will be asked to avoid caffeine and as little medication as possible 24 hours before the test.
heart failure and cardiomyopathy), coronary artery disease and heart muscle viability (with perfusion and stress testing), masses in the heart, and rare cardiac conditions. If a stress perfusion MRI test is considered patients will be asked to avoid caffeine and as little medication as possible 24 hours before the test.
A very small number of patients are claustrophobic, so they may not be able to tolerate MRI. Nevertheless, those patients can be advised to try the scanner beforehand, to bring along their favourite music or listen to their favourite radio station during the test. They can also bring a friend or family member who can stay with them inside the room. Occasionally a small dose of medication given by their physician can help them relax during the test.
Patients undergoing MRI will be asked about the presence of any metal in the body and severe kidney disease as the test may not be suitable for some.
Exercise treadmill or bike (with or without imaging) & Dobutamine stress echo
Exercise treadmill testing, or ETT for short, is performed while monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, and changes in the electric activity in the heart. The test will 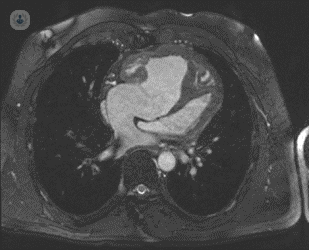 help to identify the presence of limits to coronary blood flow. If limited blood flow is identified, further tests may follow to identify the cause of the limitation. It is far better to do the exercise test combined with echo for higher sensitivity & specificity and better accuracy.
help to identify the presence of limits to coronary blood flow. If limited blood flow is identified, further tests may follow to identify the cause of the limitation. It is far better to do the exercise test combined with echo for higher sensitivity & specificity and better accuracy.
Alternatively, one can use an ergonomic bike to increase the heart rate instead of a treadmill. The advantage of the latter is that one can image the heart while the heart rate is elevated and maintained at peak exercise. However, some people cannot exercise for various reasons such as reduced or poor mobility. In that case a drug called Dobutamine, is used to induce a similar physiological response to exercise with increase in heart rate. It is expected that the patient achieves 85% maximum predicted heart rate (220 - age x 85%).
The test can also be used to assess severity of valve disease and heart muscle viability.
CT coronary angiogram (CTCA)
A cardiac computed tomography, or CT scan, is a test used to identify the presence of plaque or narrowing on the coronary artery walls. If detected, a CT scan can also indicate the severity of the narrowing of the coronary artery. The CT scan is best used to rule out coronary artery disease as the source of the symptoms being experienced.
Myocardial perfusion scan (MPS) / Nuclear stress test
A nuclear stress test is a test used to provide images of blood flow in the heart under resting conditions and during stress. Stress conditions are created either with exercise or medications that cause the heart rate to increase and or coronary arteries to dilate. The test will identify abnormal blood flow and narrowing of coronary arteries. However, as the test carries a risk of radiation other modalities may be preferred.
Coronary artery calcium scoring scan
A calcium scan is a CT scan that identifies if plaque is present and if it contains calcium within the coronary arteries. This test can be used to identify future risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attack. It is often used in individuals that have not experienced symptoms of heart disease.
If you would like to see a specialist for cardiac imaging, you can make an appointment by following this link.



