What is a bunion?
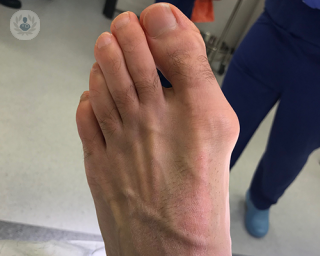
The hallux valgus or bunion is a bony deformity at the base of the big toe on the inside of the foot. It occurs when the big toe is pushed inward towards the rest of the toes, forcing the joint at the base of the foot outwards, causing the appearance of a bony lump or protrusion on the inside of the foot.

What are the symptoms of a bunion?
The main symptoms are a bulging bump in the area around the joint between the big toe and the rest of the foot, and the associated pain and inflammation, which usually get worse when walking. As the bunion grows, it will become more inflamed and uncomfortable. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling and redness around the joint on the inside of the foot.
- Calluses and corns, which develop where the big toe overlaps with the second toe.
- Reduced movement at the joint.
- Joint pain that is aggravated by the pressure of wearing shoes.
- The big toe points in the direction of the other toes.
What causes bunions?
Possible causes of bunions are:
- Genetic factors – it is thought that a certain foot type is more susceptible to bunion development.
- Arthritis is often associated with bunions
- Foot injuries
- Inappropriate footwear – the use of narrow-toed and high-heeled shoes can also force the big toe inwards and lead to the development of a bunion.
Can bunions be prevented?
To prevent bunions it is vital to pay attention to the development of our feet. When there are calluses or corns on the inside of the big toe or if you notice it is starting to point inwards, it is advisable to take some kind of measure to prevent it from getting worse. It may be impossible to prevent bunions, but the best way to lower your chances is to choose the right footwear:
- Make sure your shoes are the correct size, with room to move your toes freely
- Avoid shoes with high heels and/or pointy toes.
- Your shoes should conform to the shape of your feet.
What is the treatment?
Bunions are often manageable conditions, and non-surgical treatments to deal with the symptoms should always be tried before surgery. These include:
- Painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs
- Local application of cold, e.g. ice packs
- Bunion pads – these may be made of gel or fleece and cushion the bunion, preventing it from rubbing in the shoe. They can often be purchased over the counter. Your doctor can advise you on their use.
- Insoles, splints, and toe spacers may also help to make your foot more comfortable in your day-to-day life. Again, consult your GP or a podiatrist for advice on if and how you should use these.
- Correct footwear – make sure you are wearing roomy, comfortable shoes, with plenty of space to move your toes.
Surgey, called bunionectomy, is only indicated in severe cases where walking becomes highly difficult. Through this procedure, the surgeon can realign your toe and remove the bony protuberance and swollen tissue. However, full recovery can take weeks, or even months, and even then bunions can recur. For this reason, it is important to only wear appropriate shoes and take care of your feet after surgery.
11-13-2012 05-31-2023Bunion (hallux valgus)
Mr Matthew Solan - Orthopaedic surgery
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 05-31-2023
Edited by: Conor Dunworth
What is a bunion?
The hallux valgus or bunion is a bony deformity at the base of the big toe on the inside of the foot. It occurs when the big toe is pushed inward towards the rest of the toes, forcing the joint at the base of the foot outwards, causing the appearance of a bony lump or protrusion on the inside of the foot.

What are the symptoms of a bunion?
The main symptoms are a bulging bump in the area around the joint between the big toe and the rest of the foot, and the associated pain and inflammation, which usually get worse when walking. As the bunion grows, it will become more inflamed and uncomfortable. Other symptoms include:
- Swelling and redness around the joint on the inside of the foot.
- Calluses and corns, which develop where the big toe overlaps with the second toe.
- Reduced movement at the joint.
- Joint pain that is aggravated by the pressure of wearing shoes.
- The big toe points in the direction of the other toes.
What causes bunions?
Possible causes of bunions are:
- Genetic factors – it is thought that a certain foot type is more susceptible to bunion development.
- Arthritis is often associated with bunions
- Foot injuries
- Inappropriate footwear – the use of narrow-toed and high-heeled shoes can also force the big toe inwards and lead to the development of a bunion.
Can bunions be prevented?
To prevent bunions it is vital to pay attention to the development of our feet. When there are calluses or corns on the inside of the big toe or if you notice it is starting to point inwards, it is advisable to take some kind of measure to prevent it from getting worse. It may be impossible to prevent bunions, but the best way to lower your chances is to choose the right footwear:
- Make sure your shoes are the correct size, with room to move your toes freely
- Avoid shoes with high heels and/or pointy toes.
- Your shoes should conform to the shape of your feet.
What is the treatment?
Bunions are often manageable conditions, and non-surgical treatments to deal with the symptoms should always be tried before surgery. These include:
- Painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs
- Local application of cold, e.g. ice packs
- Bunion pads – these may be made of gel or fleece and cushion the bunion, preventing it from rubbing in the shoe. They can often be purchased over the counter. Your doctor can advise you on their use.
- Insoles, splints, and toe spacers may also help to make your foot more comfortable in your day-to-day life. Again, consult your GP or a podiatrist for advice on if and how you should use these.
- Correct footwear – make sure you are wearing roomy, comfortable shoes, with plenty of space to move your toes.
Surgey, called bunionectomy, is only indicated in severe cases where walking becomes highly difficult. Through this procedure, the surgeon can realign your toe and remove the bony protuberance and swollen tissue. However, full recovery can take weeks, or even months, and even then bunions can recur. For this reason, it is important to only wear appropriate shoes and take care of your feet after surgery.

Understanding bunion surgery: When, how, and what to expect
By Mr Naveed Shaikh
2024-11-21
Bunion surgery, also known as bunionectomy, is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting a bunion, a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. This condition can cause discomfort, pain, and difficulty in walking for many people. We invited esteemed consultant trauma and orthopaedic surgeon Mr Naveed Shaikh to shed light on the indications for bunion surgery, as well as the procedure itself, recovery, and potential outcomes. See more


Everything you need to know about bunions and bunion surgery
By Mr Garth Allardice
2024-11-21
Leading consultant orthopaedic surgeon, Mr Garth Allardice explains all about bunions and how they are treated. See more


How are bunions managed most effectively?
By Mr Kailash Devalia
2024-11-20
Here, renowned foot and ankle surgeon, Mr Kailash Devalia, delves into the medical condition hallux valgus, otherwise known as bunions. See more

Bunions: why they happen and how to get rid of them
By Mr Stefan Weitzel
2024-11-20
Bunions have the power to negatively impact several aspects of people's quality of life. Fortunately, this common problem can be successfully treated. Mr Stefan Weitzel provides you with a full explanation on why bunions happen and how to get rid of them. See more
Experts in Bunion (hallux valgus)
-
Mr Rohit Madhav
Orthopaedic surgeryExpert in:
- Sports traumatology
- Minimally invasive bunion surgery
- Ankle arthroscopy
- Tendon injuries
- Foot fracture
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
-
Mr David Redfern
Orthopaedic surgeryExpert in:
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Minimally invasive bunion surgery
- Arthritis
- Ankle replacement surgery
- Ankle arthroscopy
- Sports injuries
-
Mr Matthew Solan
Orthopaedic surgeryExpert in:
- Achilles tendon
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Heel spur
- Arthritis
- Sports injuries
- Sprained ankle
-
Mr Paul Hamilton
Orthopaedic surgeryExpert in:
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Achilles tendon
- Arthritis
- Sprained ankle
- Morton's neuroma
- Plantar fasciitis
-
Mr Edward Dawe
Orthopaedic surgeryExpert in:
- Foot and ankle
- Plantar fasciitis
- Achilles tendon
- Bunion (hallux valgus)
- Ankle replacement surgery
- Minimally invasive techniques
- See all

The Meriden Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
The Meriden Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Sussex Premier Health Hastings
Sussex Premier Health Hastings
The Ridge, St Leonards, Hastings, Saint Leonards-on-sea TN37 7RE
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Kings Park Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Kings Park Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Polmaise Road Stirling FK7 9JH
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
The Meriden Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Clifford Bridge Road, Coventry , CoventryExpert in:
- Cancer
- Cardiology
- Colorectal surgery
- Shoulder surgery
- Hand surgery
- General Surgery
-
Sussex Premier Health Hastings
The Ridge, St Leonards, Hastings, Saint Leonards-on-sea TN37 7RE, HastingsExpert in:
- Cataracts
- General Surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Diagnostics
- Ophthalmology
- Urology
-
Kings Park Hospital - part of Circle Health Group
Polmaise Road Stirling FK7 9JH, StirlingExpert in:
- Vascular Surgery
- Cardiology
- Colorectal surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurological spinal surgery
- Plastic surgery, reconstructive and aesthetics
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Joint pain
- Lumbar herniated disc
- Spinal surgery
- Minimal access surgery (keyhole surgery)
- Shoulder pain
- Osteoporosis
- Botulinum toxin (Botox™)
- Abnormal gait
- Shoulder osteoarthritis
- DEXA scan