Chloride analysis
What is being analysed in this type of test?
Chloride levels in the body are analysed to assess electrolyte balance and kidney function.
What do the results mean?
The result indicates whether chloride levels are within normal range, which is crucial for maintaining proper hydration, nerve function, and acid-base balance.
Why is the test performed?
Analysing chloride levels helps diagnose and monitor conditions such as dehydration, kidney diseases, acid-base imbalances, and certain respiratory disorders.
When to perform the analysis?
Chloride analysis is often included in routine blood tests or electrolyte panels. It may also be ordered when symptoms suggest electrolyte abnormalities or kidney dysfunction.
What type of sample is required?
A blood sample is typically required for measuring chloride levels.
Is any pre-preparation necessary?
No specific preparation is usually required before the test. However, fasting may be necessary if other tests are being conducted simultaneously.
How is the sample used?
The analysis of chloride levels helps healthcare providers diagnose and manage various medical conditions. It guides treatment decisions, such as fluid and electrolyte replacement therapies.
What are the normal values?
Normal chloride levels typically range from 96 to 106 milliequivalents per litre (mEq/L) in adults.
What does it mean to have altered values?
Abnormal chloride levels may indicate dehydration, kidney dysfunction, respiratory alkalosis, metabolic acidosis, or other underlying health issues.
Table of chloride values
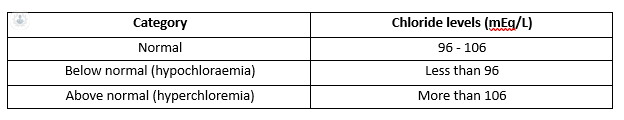
This table summarises the categories of chloride levels and their corresponding ranges, aiding in the interpretation of test results.