What is an intrauterine device (IUD)?
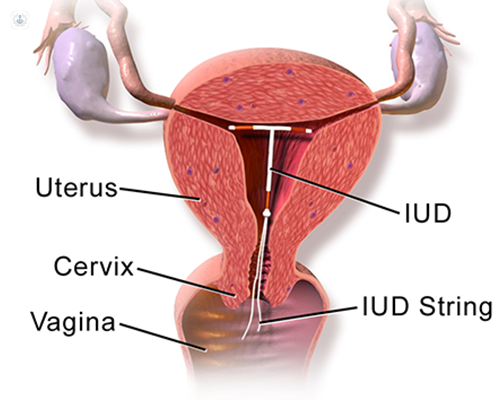
An intrauterine device, more commonly known as an IUD, is a contraceptive device. It is a small copper device that is T-shaped and inserted into the uterus. No hormones are released by this device, as copper changes the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg and survive. This change in mucus also stops a fertilised egg implanting itself. An intrauterine system (IUS), releases progesterone to prevent pregnancy.
Why would you have an IUD?
It is a highly effective contraceptive method, which is more than ninety-nine per cent effective when inserted correctly. Once it is implanted, it remains effective for 5-10 years, depending on the type used. It is not necessary to have any rest period and once it is removed, your fertility returns to normal immediately. It is important to note that whilst the IUD is a form of contraception, it does not protect you against STIs.
How is an IUD inserted?
The IUD can be inserted at any point in your menstrual cycle and will protect you from pregnancy immediately. An appointment to insert an IUD takes just thirty minutes and can be done by either a trained nurse, GP or gynaecologist. The vagina is opened using a speculum, through which the IUD is inserted into the uterus. Once the IUD is placed in the uterus, the specialist removes the speculum leaving two small cords that hang inside the vagina. The goal of the cords is to verify that the IUD is in the right place, as well as to help extract it when the time is right.
Preparation for the IUD:
Before having an IUD inserted, it is important to understand your options for contraception. IUDs are often used when you want to avoid the risks of birth control hormones, when they cannot be used, or when you want long-term protection against pregnancy.
Care after implantation:
The day of your consultation to insert the IUD, it is advisable to be accompanied by a friend, partner or family member, so that later they can take you home. Some women may have cramping, back pain in the lower back and spotting for a couple of days. It is important to have a check-up by a GP 3-6 weeks following the insertion to ensure it is placed correctly. If you have your period when it is inserted, you should avoid using tampons for the first 48 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages of the IUD:
Advantages:
- It works straight away
- It is more than 99% effective when inserted correctly
- It provides long-term protection (5-10 years)
- It is safe to use whilst breastfeeding
- No hormones are released, so there are no hormonal side effects (e.g. tender breasts, acne)
- It is not affected by other medicines or illness
Disadvantages:
- Some women experience heavier or more painful periods following IUD insertion
- There is a small risk of pelvic infection if an infection forms after the IUD fitting
- If the IUD fails and you become pregnant, there is an increased risk of having an ectopic pregnancy
Intrauterine device (IUD)
Mr Jullien Brady - Obstetrics & gynaecology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 12-19-2023
Edited by: Sophie Kennedy
What is an intrauterine device (IUD)?
An intrauterine device, more commonly known as an IUD, is a contraceptive device. It is a small copper device that is T-shaped and inserted into the uterus. No hormones are released by this device, as copper changes the cervical mucus, making it difficult for sperm to reach an egg and survive. This change in mucus also stops a fertilised egg implanting itself. An intrauterine system (IUS), releases progesterone to prevent pregnancy.

Why would you have an IUD?
It is a highly effective contraceptive method, which is more than ninety-nine per cent effective when inserted correctly. Once it is implanted, it remains effective for 5-10 years, depending on the type used. It is not necessary to have any rest period and once it is removed, your fertility returns to normal immediately. It is important to note that whilst the IUD is a form of contraception, it does not protect you against STIs.
How is an IUD inserted?
The IUD can be inserted at any point in your menstrual cycle and will protect you from pregnancy immediately. An appointment to insert an IUD takes just thirty minutes and can be done by either a trained nurse, GP or gynaecologist. The vagina is opened using a speculum, through which the IUD is inserted into the uterus. Once the IUD is placed in the uterus, the specialist removes the speculum leaving two small cords that hang inside the vagina. The goal of the cords is to verify that the IUD is in the right place, as well as to help extract it when the time is right.
Preparation for the IUD:
Before having an IUD inserted, it is important to understand your options for contraception. IUDs are often used when you want to avoid the risks of birth control hormones, when they cannot be used, or when you want long-term protection against pregnancy.
Care after implantation:
The day of your consultation to insert the IUD, it is advisable to be accompanied by a friend, partner or family member, so that later they can take you home. Some women may have cramping, back pain in the lower back and spotting for a couple of days. It is important to have a check-up by a GP 3-6 weeks following the insertion to ensure it is placed correctly. If you have your period when it is inserted, you should avoid using tampons for the first 48 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages of the IUD:
Advantages:
- It works straight away
- It is more than 99% effective when inserted correctly
- It provides long-term protection (5-10 years)
- It is safe to use whilst breastfeeding
- No hormones are released, so there are no hormonal side effects (e.g. tender breasts, acne)
- It is not affected by other medicines or illness
Disadvantages:
- Some women experience heavier or more painful periods following IUD insertion
- There is a small risk of pelvic infection if an infection forms after the IUD fitting
- If the IUD fails and you become pregnant, there is an increased risk of having an ectopic pregnancy

What is Mirena coil?
By Mr Hisham Abouzeid
2025-01-08
The Mirena coil is an intrauterine coil which releases special type of hormone called progestogen. It helps to reduce the amount of menstrual blood loss and helps with contraception. Mr Hisham Abouzeid, distinguished consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist, explains its purpose, benefits, and the best time for its insertion. See more


T marks the spot: what is complex coil removal?
By Dr Grisham Smotra
2025-01-08
In this latest article, a consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist shares their expert insight about when removing a contraceptive coil may need a little more elbow grease than a standard removal. See more


What’s the best treatment for fibroids?
By Ms Eleni Mavrides
2025-01-08
Uterine fibroids, or non-cancerous growths in the uterus, can cause a range of symptoms including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain and pressure on surrounding organs. In this article, leading consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist Ms Eleni Mavrides answers the question: “What’s the best treatment for fibroids?”. See more


Is heavy menstrual bleeding affecting your quality of life? Menstrual disorders explained
By Ms Pushpakala Maharajan
2024-12-23
Menstrual disorders which cause heavy or irregular periods can affect women's quality of life greatly. In this article, highly esteemed consultant obstetrician and gynaecologist Ms Pushpakala Maharajan expertly explains the causes and treatment options for the most common menstrual disorders. See more
Experts in Intrauterine device (IUD)
-
Miss Christine Robinson
Obstetrics & gynaecologyExpert in:
- Contraceptive methods
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Menopause
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
-
Dr Georgina Forbes
Genitourinary MedicineExpert in:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Contraceptive methods
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Thrush
- Sexual health
- Genital warts
-
Dr Alisha Esmail
Obstetrics & gynaecologyExpert in:
- Gynaecological examination
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- Menopause
- Menstrual disorders
- Sexual health
- Women's health
-
Ms Rhonda Flemming
Obstetrics & gynaecologyExpert in:
- Early pregnancy
- Endometrial polyps
- Gynaecological examination
- Heavy periods
- Hysteroscopy
- Intrauterine device (IUD)
- See all

London Gynaecology - The Portland Hospital
London Gynaecology - The Portland Hospital
212 Great Portland Street London W1W 5QN
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

London Gynaecology- The City of London
London Gynaecology- The City of London
15 Austin Friars, London EC2N 2HE, United Kingdom
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Oak Tree Clinic
Oak Tree Clinic
2A, Oak Tree Court Mulberry Drive, Cardiff Gate Business Park, Cardiff
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
London Gynaecology - The Portland Hospital
212 Great Portland Street London W1W 5QN, Central LondonExpert in:
- Miscarriage
- Thrush
- Colonoscopy
- Maternity care
- Ultrasound
- Pregnancy
-
London Gynaecology- The City of London
15 Austin Friars, London EC2N 2HE, United Kingdom, Central LondonExpert in:
- Miscarriage
- Cancer screening clinic
- Ultrasound
- Pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Fibroids
-
Oak Tree Clinic
2A, Oak Tree Court Mulberry Drive, Cardiff Gate Business Park, Cardiff, CardiffExpert in:
- Minimal access surgery (keyhole surgery)
- Ultrasound
- Endometriosis
- Chronic diseases
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- Fertility
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Menopause support
- Alzheimer's disease
- Tubal factor infertility
- Cluster headaches
- Tension headache
- Chronic headache
- Complex endometriosis
- Fertility preservation
- Female infertility
- Ovulatory disorders







