What is fixed prosthodontics?
Fixed prosthodontics (also known as “indirect restorations”) is an area of dentistry that involves replacing teeth with fixed dental prostheses.
There are various kinds of fixed prosthodontics:
- Crowns – also referred to as “caps”, these are attached to what is left of a damaged tooth, providing coverage and protection to the remaining natural tooth structure and simultaneously replacing the part of the tooth that was lost. Crowns can be made of a variety of materials, from metal to ceramic, and the type of crown used depends on the type of tooth, how much of the tooth has been lost, and the patient’s preference.
- Bridges – designed to restore gaps between teeth, bridges often restore a natural appearance. They may be attached to a metal wing, or possibly to an adjacent crowned tooth to hold them in place.
- Veneers – relatively thin pieces of ceramic or resin that are glued onto the surface of damaged teeth to improve their aesthetic appearance.
- Inlays – more conservative than a crown, an inlay sits within the cusps of a tooth
- Onlays – similar to inlays, but cover, strengthen and reinforce the cusps, rather than the area between them.

Why is it done?
Fixed prostheses are used to replace lost or damaged teeth, providing the patient with a fixed tooth with which they can chew and speak normally, providing the same functions as a normal tooth. They also restore a pleasing aesthetic appearance.
What does fixed prosthodontics consist of?
Fixed prosthodontics are typically made in a laboratory after the dentist takes an impression (mould) of the patient’s teeth so that the prostheses are made to fit each specific patient. Once the prosthesis is created, it will be placed in the patient’s mouth by the dentist.
Part of the remaining tooth structure usually has to be removed to make room for the thickness of the prosthesis. The amount that must be removed depends on the material of that prosthesis.
What is recovery like after the intervention of fixed prosthesis?
The care after the intervention depends on the type of prosthesis that will be placed on the patient. After the procedure, the patient should eat soft foods, avoiding hot or particularly cold food, as their teeth may be sensitive.
04-27-2017 06-13-2023Tooth replacement
What is fixed prosthodontics?
Fixed prosthodontics (also known as “indirect restorations”) is an area of dentistry that involves replacing teeth with fixed dental prostheses.
There are various kinds of fixed prosthodontics:
- Crowns – also referred to as “caps”, these are attached to what is left of a damaged tooth, providing coverage and protection to the remaining natural tooth structure and simultaneously replacing the part of the tooth that was lost. Crowns can be made of a variety of materials, from metal to ceramic, and the type of crown used depends on the type of tooth, how much of the tooth has been lost, and the patient’s preference.
- Bridges – designed to restore gaps between teeth, bridges often restore a natural appearance. They may be attached to a metal wing, or possibly to an adjacent crowned tooth to hold them in place.
- Veneers – relatively thin pieces of ceramic or resin that are glued onto the surface of damaged teeth to improve their aesthetic appearance.
- Inlays – more conservative than a crown, an inlay sits within the cusps of a tooth
- Onlays – similar to inlays, but cover, strengthen and reinforce the cusps, rather than the area between them.

Why is it done?
Fixed prostheses are used to replace lost or damaged teeth, providing the patient with a fixed tooth with which they can chew and speak normally, providing the same functions as a normal tooth. They also restore a pleasing aesthetic appearance.
What does fixed prosthodontics consist of?
Fixed prosthodontics are typically made in a laboratory after the dentist takes an impression (mould) of the patient’s teeth so that the prostheses are made to fit each specific patient. Once the prosthesis is created, it will be placed in the patient’s mouth by the dentist.
Part of the remaining tooth structure usually has to be removed to make room for the thickness of the prosthesis. The amount that must be removed depends on the material of that prosthesis.
What is recovery like after the intervention of fixed prosthesis?
The care after the intervention depends on the type of prosthesis that will be placed on the patient. After the procedure, the patient should eat soft foods, avoiding hot or particularly cold food, as their teeth may be sensitive.

Restoring smiles: Modern solutions for toothlessness
By Dr Karolina Wolowiec
2024-12-30
Toothlessness, or edentulism, refers to the condition of having no natural teeth remaining. This can be a challenging and distressing situation, affecting both oral function and appearance. Thankfully, modern dentistry offers several solutions to restore a functional and aesthetic smile. See more


The dos and don’ts following a tooth extraction
By Dr Moira Wong
2024-12-30
Though aftercare may differ depending on the type of procedure, there are some general things you should and shouldn't do after having a tooth removed which will either help or delay your recovery. Dr Moira Wong, a leading orthodontist based in London with extensive experience in dentistry, offers some dental dos and don’ts following tooth extraction. See more
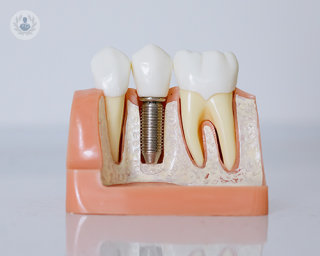

All about dental implants
By Dr Sahil Patel
2024-12-30
Dental implants are a common solution for missing teeth, offering long-lasting, functional, and natural-looking results. Here, Dr Sahil Patel, renowned cosmetic dentist based in London, offers an expert insight into dental implants. See more
Experts in Tooth replacement
-
Dr Dinesh Vegad
DentistryExpert in:
- Dental implants
- Guided implant surgery
- Immediate loading implants (Teeth in a day)
- Tooth replacement
- Dental bone grafts
- Dental implants maintenance
-
Dr Amit Mohindra
DentistryExpert in:
- Dental implants
- Immediate loading implants (Teeth in a day)
- Guided implant surgery
- Tooth replacement
- Conscious sedation
- Peri-implantitis
-
Dr Sahil Patel
DentistryExpert in:
- Cosmetic dentistry (aesthetic dentistry)
- Veneers
- Invisalign
- Complex restorative dentistry
- Smile design
- Tooth replacement
-
Dr Krisztina Papp
DentistryExpert in:
- Tooth replacement
- Root canal treatment
- Teeth whitening
- Dental crown
- Dentures
- Complex restorative dentistry
-
Dr Nikolaos Kasiteridis
DentistryExpert in:
- Tooth replacement
- Dental crown
- Dentures
- Teeth whitening
- Veneers
- Root canal treatment
- See all

One To One Dental Clinic (121)
One To One Dental Clinic (121)
80 Harley Street
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

Forest & Ray - Dentists, Orthodontists, Implant Surgeons
Forest & Ray - Dentists, Orthodontists, Implant Surgeons
8F Gilbert Pl, London, WC1A 2JD
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors

The White Bridge Clinic
The White Bridge Clinic
140 Oxford Rd, Kidlington OX5 1DZ
No existe teléfono en el centro.
By using the telephone number provided by TOP DOCTORS, you automatically agree to let us use your phone number for statistical and commercial purposes. For further information, read our Privacy Policy
Top Doctors
-
One To One Dental Clinic (121)
80 Harley Street, Central LondonExpert in:
- Dental Implants (replacing teeth)
- Orthodontics
- SMILE
-
Forest & Ray - Dentists, Orthodontists, Implant Surgeons
8F Gilbert Pl, London, WC1A 2JD, Central LondonExpert in:
- Braces
- Porcelain veneers
- Crowns
- Cosmetic dentistry
- Dental implants
- Orthodontics
-
The White Bridge Clinic
140 Oxford Rd, Kidlington OX5 1DZ, OxfordExpert in:
- Cosmetic dentistry
- Dental implants
- Peri-implantitis
- See all
- Most viewed diseases, medical tests, and treatments
- Snoring
- Chronic headache
- Botulinum toxin (Botox™)
- Platelet-rich plasma
- Cleft palate
- Tooth wear
- Tooth sensitivity
- Tooth abscess
- Facial pain
- Dental phobia







