Gout
Professor Hasan Tahir - Rheumatology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 06-20-2023
Edited by: Conor Dunworth
What is gout?
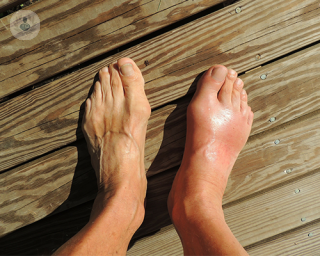
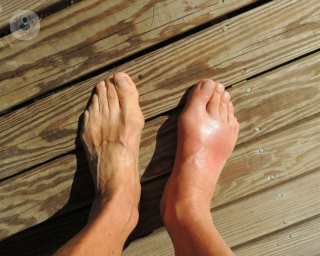
Gout is a type of arthritis that appears when there is a build-up of uric acid in the blood which causes joint swelling. If urate serum levels exceed the physiological zone of saturation (around 7.6 mg/dl), monosodium urate crystals form and are stored in the cartilage and periarticular tissues of the peripheral joints.
From a clinical perspective, the continued deposit is silent, and almost 10 per cent of patients have hyperuricemia, which will more than likely lead to clinical gout. Acute gout is a very painful condition that affects just one joint. Chronic gout involves multiple attacks, and, quite often, more than one joint is affected.

What is the prognosis of gout?
If the disease is diagnosed at an early stage, the affected individual can lead a normal life if they follow the prescribed treatment correctly. For older people affected by gout, reducing uric acid levels in the blood could help the tophi disappear and improve joint movement.
Broadly speaking, gout carries with it more complications when symptoms develop in a patient who is under the age of 30. Metabolic syndrome and heart disease contribute to early death in people with gout.
What are the main symptoms?
There are numerous symptoms that patients suffering from acute gout may experience. Typically, only some joints are affected. The joints that tend to be affected are the big toe, the knee, or the ankle. In many cases, an intense, throbbing and unbearable pain can come on suddenly at night. Other main symptoms of gout include the following:
- hot, red, and swollen joint
- fever
After the first attack, gout patients don’t normally have any symptoms. However, many people will have another attack in the following six to 12 months. Some patients may develop chronic gout, also known as gouty arthritis. This type of gout can cause joint damage and a loss of joint movement. People with this kind of gout quite often have joint pain and other associated symptoms most of the time.
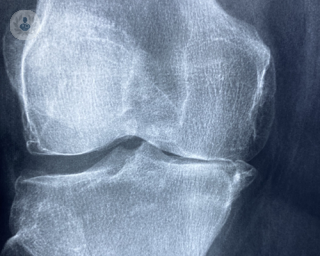
What tests are performed to test for gout?
There are several medical tests to diagnose gout. They include:
- synovial fluid analysis
- a test for uric acid in the blood
- joint X-ray
- synovial biopsy
Does a high level of uric acid always indicate gout?
A level of uric acid that is higher than 7ml/dl in the blood is deemed high. However, not everyone with high levels of uric acid has gout.
What causes gout?
Gout is caused by higher-than-normal levels of uric acid. This happened when the body produces too much uric acid or when the body is unable to get rid of the uric acid. When there is too much uric acid in the fluid around the joints, uric acid crystals form.
These crystals cause joint swelling and pain as well as an increase in temperature in the surrounding area. The main cause of gout remains unknown. The disease is thought to be hereditary, and men, postmenopausal women, and alcoholics, are more susceptible to it.
Is there any way that it can be prevented?
It is thought that gout can’t be prevented. There are, however, certain risk factors that can make symptoms appear. Taking medications to reduce levels of uric acid can prevent gout from progressing.
How exactly is gout treated?
It is recommended that the patient see a specialist and start taking the medication for gout as soon as possible to lessen symptoms if having an attack. Anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen and indometacin are also recommended. If symptoms worsen, the dose should be increased.
The patient will need different types of medication if they have:
- several attacks the same year or high intensity attacks
- joint damage
- tophi
- kidney disease or kidney stones
Another effective treatment is to make diet and lifestyle changes to avoid gout attacks. Patients should reduce their alcohol consumption (especially beer), lose as much weight as possible, exercise regularly, and reduce consumption of red meat and sugary drinks.

Which specialist should I see if I have gout?
The specialist who treats gout is a rheumatologist. They are often also the specialist responsible for correctly diagnosing the patient and starting them on a treatment which could reduce uric acid levels in the blood so that the urate crystals dissolve.
Can gout be cured? If so, how?
Rheumatologists believe that gout can be cured, and to achieve this, the levels of uric acid in a patient's blood should be enough to dissolve the crystals. The symptoms should disappear and there shouldn’t be any long-term damage to joints.
What foods and drinks can help avoid gout attacks?
Patients who have had a history of gout are encouraged to consume dairy products, vegetables, nuts, pulses, fruits, and whole grains (ones with less sugar). Drinking coffee and taking vitamin supplements can help some people.
When are men and women typically diagnosed with gout?
In the majority of cases, men are typically diagnosed with gout in their late 40s and in their 50s, whilst women tend to be, more often than not, diagnosed with the joint-affecting condition after they have experienced menopause.
What are the main associated risk factors?
Clinical research that has been conducted on gout has suggested that genetics can play quite an important role when it comes to certain people being more at risk of developing gout than others. People with the following diseases have a higher chance of developing gout:
- diabates
- kidney disease
- obesity
- sickle cell anaemia and other types of anaemia
- leukaemia and other blood cancers
Gout may also develop after taking medications that prevent the elimination of uric acid. People who take medications such as hydrochlorothiazide and other diuretics are more likely to have higher levels of uric acid in the blood. As a person ages, their chances of developing gout increases.
People who have recently experienced some form of trauma or who have undergone some form of surgery are also at a higher risk of suffering from gout.
How long does gout last?
Patients who are diagnosed with chronic gout will experience its related symptoms throughout their lifetime, but patients who get an acute gout diagnosis will usually only suffer painful and uncomfortable joint pain and swelling for anywhere between seven to 12 days.
What happens if gout is left untreated?
If gout is left untreated, and if a patient with either chronic or acute gout does not receive the adequate treatment, they can suffer from permanent damage to their bones, joints, and tissues. Gout that progresses without treatment can also have a negative effect on sexual function, emotional health, sleep, as well as social interactions.
If one's uric acid levels remain higher than is considered to be normal, they are at a higher risk of suffering from health conditions such as kidney stones, stroke, heart attack, and chronic kidney disease.