High blood pressure diet
What is the hypertension diet?
The hypertension diet is recommended for patients suffering from arterial diseases. Hypertension is high blood pressure and is a common condition in which the force of blood being pumped throughout the body is high, and can have serious consequences of cardiovascular health. Blood pressure is considered to be high when the value is 140 mmHg systolic and 90 mmHg diastolic or higher.

Why is a special diet for hypertension needed?
This type of diet is followed when a patient has high blood pressure (hypertension). Due to the serious medical conditions that can result from long-term hypertension, it is recommended along with other measures, to follow a specific diet to reduce blood pressure levels. People who are more at risk of having hypertension are those with high cholesterol, diabetes, stress, and those who are overweight.
What is the hypertension diet?
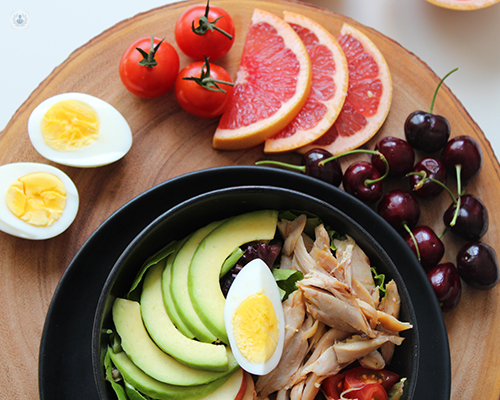
The aim of such diets is to reduce the chances of high blood pressure and to improve food habits as well. The main recommendation for a blood-pressure-friendly diet is to reduce the amount of salt ingested with each meal. The body needs 1.25g of salt daily and the maximum dose that we should consume is the equivalent of a teaspoon of coffee (6g), taking into account that most foods already contain salt. The consumption of pre-cooked or packaged products such as soups, pizzas or sausages as well as energy drinks, especially coffee should be avoided. Alcohol and tobacco are also risk factors for the onset of hypertension. The best dietary regime to follow is a diet rich in vegetables, fruit and in general, foods that contain little fat.
Preparing for a hypertension diet
There are a number of helpful tips to cook food with less salt, such as cooking potatoes with their skin and boiling them without salt. It is also recommended to only add salt to meats when they have been browned or roasted, in addition to steaming or using aluminium foil when cooking food to help preserve the flavour of the food, and reducing the temptation to add salt to food to add flavour.
The use of salt substitutes to give more flavour to the meat can be helpful as well, such as adding nutmeg, thyme, garlic, onion, oregano or rosemary. When cooking fish, you can use curry powder, dill, mustard or lemon juice. For vegetable dishes, you could add rosemary, sage, cinnamon, tarragon or basil. Dairy products, low-fat meats, fish, eggs and low-sugar cereals are all recommended. For drinks, water, tea, juices and unsweetened soft drinks are recommended.
It is important to pay attention to the type and amount of fats that are ingested. Therefore, it is best to avoid animal fats such as butter, bacon or lard. Choose fats with a high level of poly-unsaturated or mono-unsaturated fatty acids such as sunflower, olive, rapeseed, flax or soybean oil.