Kidney biopsy
What is a kidney biopsy?
A kidney biopsy (or renal biopsy) is a diagnostic test in which the nephrologist extracts a small piece of tissue from the patient’s kidney to examine in a laboratory for signs of disease or kidney damage.
Why is a kidney biopsy done?
A kidney biopsy may be performed to diagnose or determine the severity of a suspected kidney problem, to monitor treatment, or to monitor the health of a transplanted kidney. A doctor may recommend a kidney biopsy based on:
- Blood in the urine (haematuria)
- Excessive or increased protein in the urine (proteinuria)
- Excessive waste products in the blood caused by problems in kidney function
What does a kidney biopsy consist of?
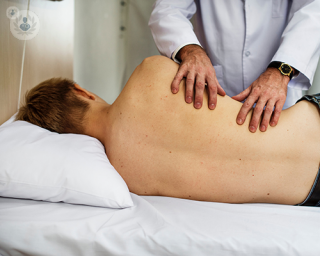
A kidney biopsy involves extracting a piece of tissue from the kidneys for later examination under a microscope. The most common procedure is called percutaneous kidney biopsy. The patient is given local anaesthesia and a needle is inserted through the skin into one of the kidneys, guided by ultrasound. The needle is used to extract the tissue sample and may need to be inserted more than once to extract sufficient tissue.
In some cases, for example if the patient has a bleeding disorder, a laparoscopic (minimally invasive) biopsy may be conducted instead, using a small incision and a thin tube equipped with a light and a camera (laparoscope), through which the doctor can cut a sample.
The patient must remain in the hospital for one night, resting completely. If there are no complications the following day, the patient will be discharged.
Preparation for kidney biopsy
Before undergoing a kidney biopsy, the patient should inform the specialist of the following:
- Medications you are taking, even if they are herbs or vitamin supplements
- If you have any allergies
- If you have bleeding problems or take anticoagulant medications
- If you are or think you may be pregnant
In addition, the doctor may also recommend that the patient stop taking solid or liquid foods before the biopsy.
How does it feel during the examination?
The patient is awake during a kidney biopsy, lying on their abdomen or on their side. Local anaesthesia is used, so the patient feels little to no pain. After waking up, the anaesthetised area may feel slightly sensitive for a few days.